NB-IoT ou Narrowband IoT est un nouveau standard de communication Low Power Wide Area Network (LPWAN ou Réseau basse consommation longue portée) spécialement conçu pour l’Internet des objets (Internet Of Things) développé par 3GPP (Third Generation Partnership Project, l’organisation derrière la standardisation des réseaux cellulaires).
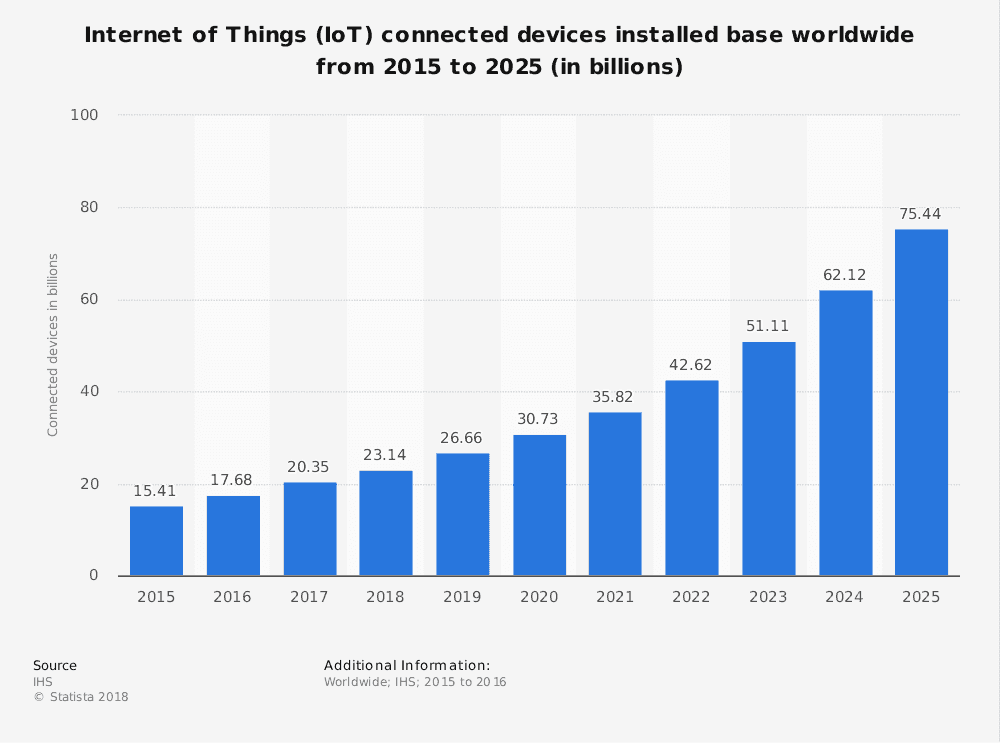
Avec l’avènement de l’IoT, les problématiques liées à l’industrie 4.0 et la prédiction des experts d’avoir plus de 75 Milliards d’objets connectés à l’aide d’un réseau sans fil d’ici 2025, il est nécessaire de créer des technologies adaptées à ces nouveaux besoins. Ce standard permet aux objets connectés de communiquer de gros volumes de données sur de très grandes distances avec une latence très élevée.
Certains annoncent même que cette technologie représente le futur des standards de communication IoT et sera celui le plus utilisé d’ici 2025.
Nous allons donc vous présenter ce nouveau standard en détail afin d’appréhender les avantages pour l’IoT.
NB-IoT en détails
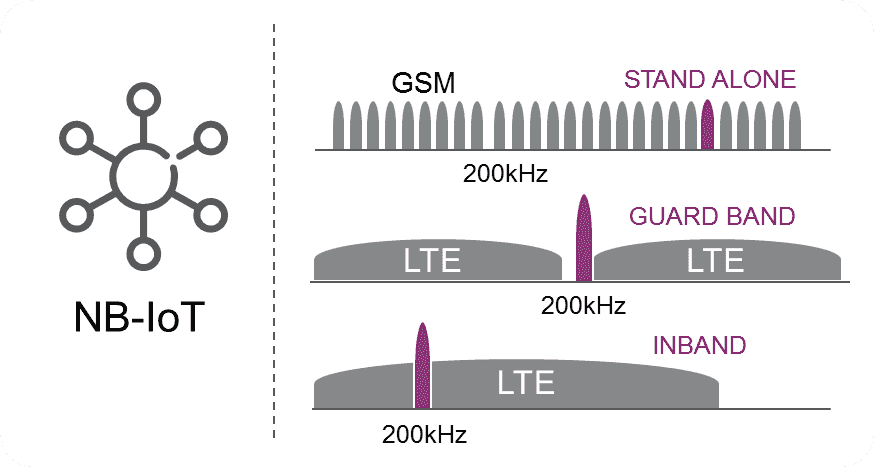
NB-IoT ou Narrowband IoT ou encore appelé LTE-M2 est une technologie basse consommation et longue portée (LPWAN) validée en Juin 2016 qui peut fonctionner de trois manières différentes:
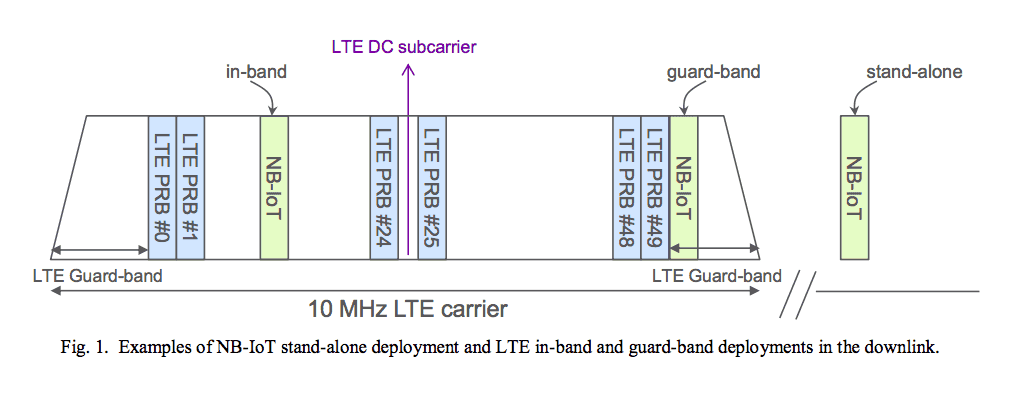
- Sur la bande de fréquence 200 kHz anciennement le réseau GSM
- Avec le réseau LTE qui réserve des ressources pour NB-IoT
- Au sein d’un réseau indépendant
Le spectre de fréquence GSM de 200kHz est peu utilisé aujourd’hui et laisse donc potentiellement la place, pour ce type de technologie, d’apporter une nouvelle solution LPWAN.
Tout comme LoRa et Sigfox, ce standard permet à des objets basse consommation de communiquer avec des applications externes à travers le réseau cellulaire.
Le constructeur Chinois Huawei est un fervent défenseur de cette technologie déjà disponible en Chine. Il a fortement contribué ces dernières années dans la définition technique de cette technologie.
Echange d’un grand volume de données
A la différence de LTE-M, il n’est pas basé sur le protocole IP mais utilise tout de même un protocole basé sur l’échange de message (message based). Il a pour avantage de proposer un taux de modulation plus rapide que LoRa ou Sigfox. Il peut donc échanger une plus grande quantité de données à un rythme moins élevé. LTE-M quant à lui, est plus adapté à des applications qui nécessitent une plus grande bande passante.
Une latence élevée
Techniquement NB-IoT utilise donc la bande de fréquence de 200kHz et la modulation OFDM pour les communications entrantes et SC-FDMA pour les communications sortantes. Par son design, il n’est pas prévu d’avoir des temps de réponse de l’ordre de la milliseconde.
Il permet d’avoir des débits de 20 à 250Kbit/s en download ou upload avec une latence inférieure à 10 secondes environ. La latence (latency), dépendra de la qualité de la puce de communication, du réseau, de la qualité de réception et de la distance avec l’antenne la plus proche.
Utilisation des réseaux mobiles existants
NB-IoT s’appuie sur les réseaux 4G existants dont un certain nombre de fonctionnalités et mécanismes sont hérités. Il est donc compatible avec une mobilité à l’international grâce à l’itinérance aussi appelé roaming. Cela signifie aussi que ces réseaux sont accessibles sous licence et sont pilotés par des opérateurs spécialisés dans le domaine. La qualité du réseau est donc gérée par des experts du métier.
NB-IoT est considéré 5G ready, c’est à dire qu’a sa sortie il pourra être compatible avec cette nouvelle norme de transmission.
Nous sommes donc face à une technologie qui est loin d’être temps réel à cause de sa grande latence. Les cas d’utilisation sont donc pour des besoins qui ne nécessitent pas ce type de contrainte.
Les avantages de NB-IoT
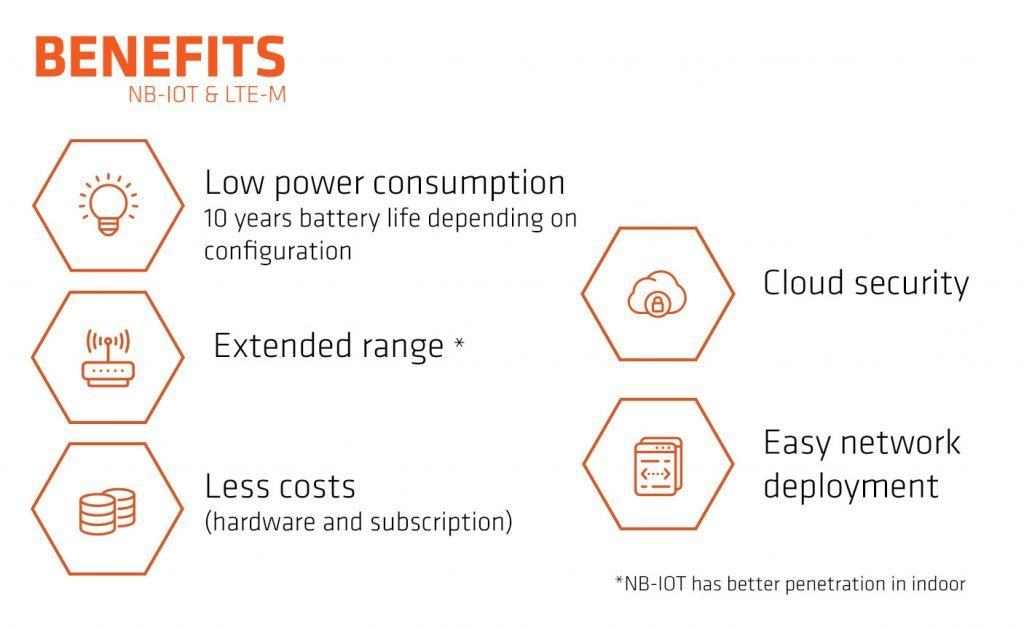
Cette nouvelle technologie apporte un certain nombre d’avantages par rapport à son domaine d’utilisation.
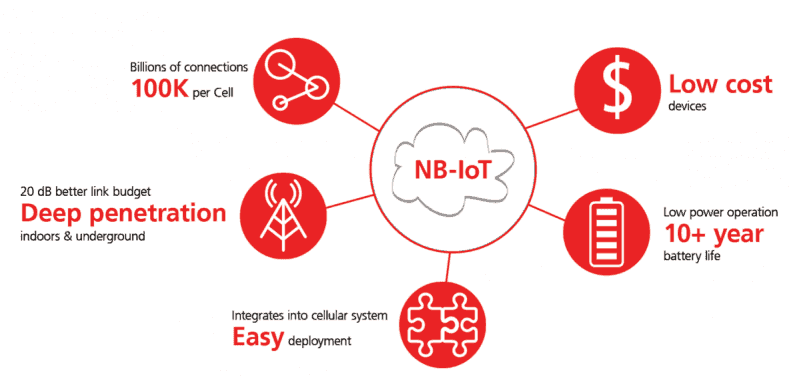
La faible consommation
Le premier point critique dans le domaine des objets connectés est la consommation électrique. Comme vu plus haut, le nombre de devices intelligents ne fait qu’augmenter. Il est donc primordial que ces supports consomment le moins possibles pour plusieurs raisons:
- Lutter contre la surconsommation électrique
- Il n’est pas envisageable de recharger ou changer des batteries d’un tel nombre d’IoT
- Pourquoi consommer de l’énergie alors que ce n’est pas nécessaire ?
Cette technologie est dites LPWAN donc répond aux standards de consommation minimale.
La fiabilité
La communication de ces objets via NB-IoT n’est certes pas temps réel mais se doit d’être fiable dans le temps. En s’appuyant sur des réseaux existants et sous licence, les opérateurs sont déjà en charge de la qualité de service de ceux-ci. Ils pourront ainsi garantir une QoS (Quality Of Service) suffisante pour ce type de fonctionnement.
Diminution des coûts
La simplicité du standard sur lequel repose cette technologie permet de créer des puces de communication peu onéreuses. En effet, une puce qui supporte uniquement NB-IoT est beaucoup moins chère à produire qu’un module qui implémente LTE-M par exemple. De plus, le fait d’être orienté très faible consommation, c’est encore une économie substantielle.
Contrairement à certains autres technologies, il n’y a aucunement besoin d’une passerelle (gateway) pour que cela fonctionne.
Une couverture plus adaptée
Reposant sur le réseau actuel de la 4G ce mode de communication est aussi bien adapté pour une utilisation en intérieur (Indoor) ou en extérieur. Ainsi la seule problématique, quand il sera implémenté, sera de vérifier la couverture des localisations de vos devices IoT.
Cas d’utilisations
Ce standard a été pensé pour de nombreuses applications et cas d’utilisation pour le domaine de l’IoT et l’IIoT (Industrial Internet Of Things). On retrouve entre autre:
- Les objets pour la mesure intelligente comme pour l’électricité, le gaz ou l’eau (compteur d’eau) par exemple
- Les systèmes de surveillances comme les alarmes ou les alarmes incendies
- Les villes connectées ou smart city qui permet de piloter par exemple les lampes, le mobilier urbain ou encore le suivi du remplissage des poubelles
- La mesure des données de santé personnelles à l’aide d’objets connectés
- Le domaine médical trouvera un avantage certain pour la surveillance des constantes de santé à distance comme le montre le document disponible ici.
- L’état de certaines machines industrielles qui ne nécessitent pas un fonctionnement temps réel
- …
Il existe de nombreux cas d’utilisations auquel répond NB-IoT. Les cas présentés ci-dessus se veulent réels et sont des problématiques ou des sujets de réflexion actuels. Mais de manière générale tout objet connecté qui aurait besoin de communiquer sur de longues distances et qui ne nécessitent pas des temps de réaction trop rapides pourraient être concernés.
Advantech commence dores et déjà à créer des solutions d’acquisition de données ou de communication industrielle qui implémentent NB-IoT. Vous pouvez les retrouver sur cette page.
Etat du déploiement de NB-IoT
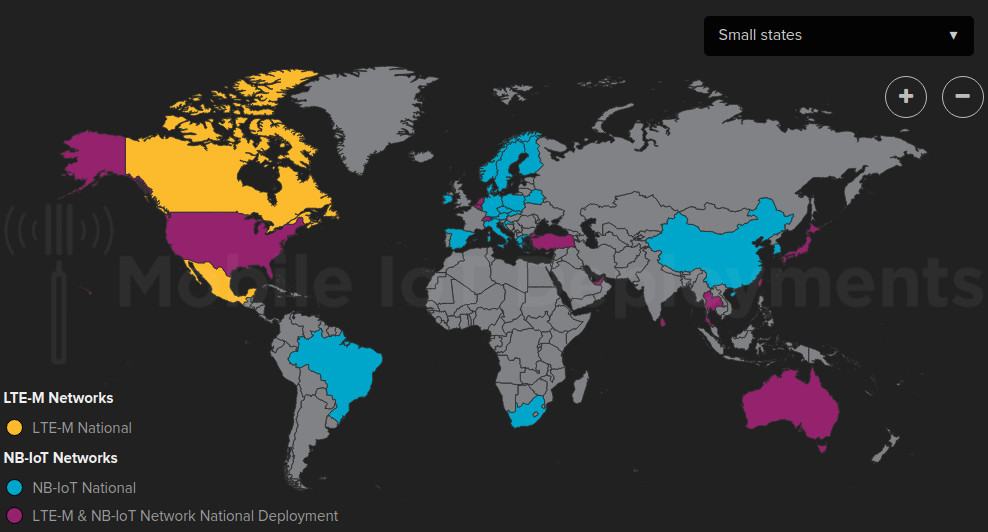
NB-IoT ne peut fonctionner « out of the box » sur le réseau actuel 4G sans l’implémentation du standard par les opérateurs en charge de la couverture mobile du territoire qui vous concerne.
Aujourd’hui la France n’a toujours officiellement lancé aucun réseau qui implémente cette nouvelle technologie. Donc NB-IoT n’est, pour le moment, officiellement pas disponible en France. Cependant l’opérateur SFR travaillerait sur ces sujets en partenariat avec des industriels du secteur. Orange, quant à lui, a lancé des zones de tests pour LTE-M mais aucun travaux sur NB-IoT semble en cours (Alors qu’ils ont déployés NB-IoT en Belgique)
Pour rappel la France a vu naître deux technologies concurrentes à savoir Sigfox et LoRa ce qui explique l’état de déploiement actuel de NB-IoT.



Commentaires récents